In recent years, we have witnessed the emergence of many hot trends and movements. These trends include DeFi, Metaverse, GameFi, NFTs, AI, and meme cryptocurrencies. Currently, the latest trend seems to revolve around meme cryptocurrencies. However, many have noticed a rising star known as DePIN. So, what exactly is DePIN? What are some examples of DePIN, and what are the benefits and limitations associated with this type of token? This article will explore all of that.
What is DePIN?
Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks (DePIN), also known as DePIN, have become a new trend in the cryptocurrency space. DePIN refers to new networks that utilize tokens as a motivator for the community to build physical infrastructure. This is where DePIN differentiates itself from traditional cryptocurrencies because DePIN requires some form of physical hardware.
DePIN also employs tokens or coins to incentivize people to participate in the network and contribute to building the infrastructure from scratch. This leads to the creation of “Real-World Dapps.” DePIN utilizes blockchain technology to merge real-world physical infrastructure with permissionless and trustless hardware networks.
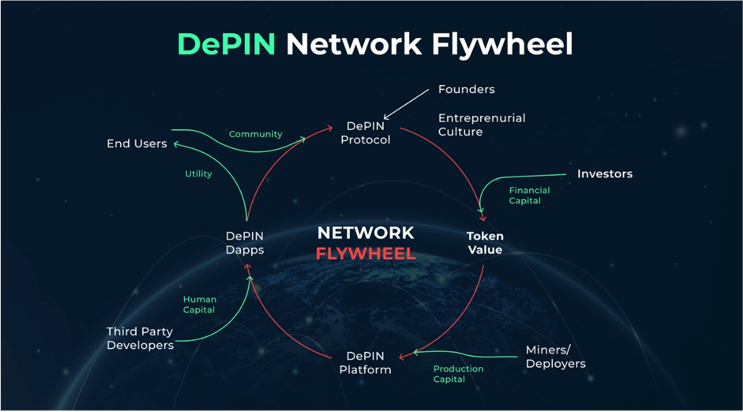
While DePIN has the potential to deliver faster results compared to traditional companies due to significantly lower initial costs, almost no barriers to entry, and financial components in the form of incentives for anyone participating in the network, DePIN also represents a slow revolution. In the long run, it can empower users and network participants with ownership and control, while providing them with opportunities to earn hundreds, if not thousands, of dollars annually.
In summary, DePIN is a decentralized network dividing traditional physical hardware infrastructure that requires significant capital. They also allow anyone to become an operator or hardware provider, thus solving the liquidity problem through token-encoded incentives and peer-to-peer markets.
The Importance of Token Incentives: Token incentives play a vital role in two stages throughout the entire process. First, DePIN uses tokens to incentivize people to participate in the network from the beginning, aiding the project's initial launch. Second, it motivates new users to join afterward as the network effect ensures the earlier they participate, the better their financial outcome.
Looking Back at the History of DePIN
The spread of DePIN may appear fresh, but there have been various similarities in the past. Projects like Helium and Filecoin, created in 2019 and 2020 respectively, can be considered early examples of DePIN. However, it wasn't until late 2022 that these tokens were specifically labeled as DePIN in Messari's research report and through a Messari Twitter poll.
⏩ https://twitter.com/MessariCrypto/status/1588938954807869440?s=20
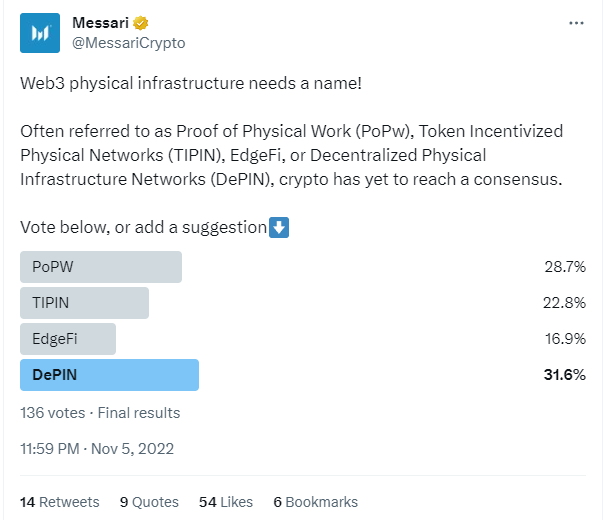
Prior to that, the projects currently classified as DePIN were referred to by different names such as EdgeFi, Proof-of-Physical-Work (PoPW), or Token Incentivized Physical Networks (TIPIN). Thus, determining the true origin of this segment is challenging. However, Messari decided to consolidate all these names into a common group and started classifying all these projects under the same new acronym – DePIN. Since then, the popularity surrounding these projects seems to have only grown. Many have claimed that DePIN is a real-world use case and innovation that blockchain technology can bring. Some have even gone as far as declaring it as the only case. However, in reality, these projects operate differently.
Types of DePIN
According to the previously mentioned Messari report, when referring to DePIN, people usually describe projects falling into one of the following four categories:
Cloud Storage Networks: Including file storage, servers, VPN networks, or CDNs. Wireless Networks: Community-driven networks, which may include technologies like 5G or LoRaWAN. Sensor Networks: Anything from weather to mapping, including real-time data collection through sensors. Energy Networks: Primarily distributed electricity grids. These are just the main categories described by Messari. However, that doesn't mean the potential of DePIN is limited to these four categories. As we'll see in the later benefits section, DePIN has a long list of potential advantages that can be applied to anything, where the four main factors (hardware, hardware operators, tokens, and users) in DePIN will be present.
How Does DePIN Work?
For DePIN to function correctly and smoothly, there need to be four different participating entities or parties in the network. They are:
Hardware: A physical component connecting the network to the physical world. Hardware Operators: Individuals who purchase or lend their hardware in the process of connecting to a specific network. Token: A form of financial incentive, often a specific cryptocurrency of the project. Tokens are rewarded to hardware operators based on established rules set by the project. Users: Last but not least, DePIN requires users within the infrastructure to utilize the network's hardware. These are people willing to use and pay for the solutions and services provided by DePIN. If any of these entities are missing in any business model or DePIN concept, the project can become immediately threatened or fail. Similarly, if there aren't enough entities present in the project's initial stage, its future becomes uncertain and risky.
Specific factors such as reward size or hardware barriers may vary from one project to another. Therefore, they can be difficult to categorize or divide into specific groups. However, identifying which projects fall into the DePIN world becomes relatively straightforward.
Examples of DePIN
As mentioned earlier, the history of DePIN is quite elusive. One can speculate about the first DePIN projects or the history of this cryptocurrency subsector as much as they desire, but that won't change the fact that there are projects within this category. While the list of these projects is extensive, with Helium arguably being one of the first projects, we'll only briefly summarize a few of the most well-known projects that can be classified as DePIN.
- Filecoin (FIL) is a project that provides cloud storage services similar to Google Cloud or Amazon Web Services in Web2. It offers a decentralized and secure storage solution incentivized by the FIL token. Filecoin connects those in need of data storage space with individuals who have spare hard drive space.
- Dimo (DIMO) is a project that provides media and user-driving data marketing capabilities. After users download the Dimo app, they can choose what information about their vehicle (such as battery health) they will share, and they are rewarded with DIMO tokens. There is a significant automotive market for various entities such as ride-sharing apps to purchase access to this data and improve their operations.
- Hivemapper (HONEY) is a decentralized mapping platform built by users with cryptocurrency-enabled cameras mounted on cars. It aims to recreate Google Street View but in a decentralized manner. Users drive with these cameras and generate GPS-related image data that can be financially rewarded with HONEY tokens.
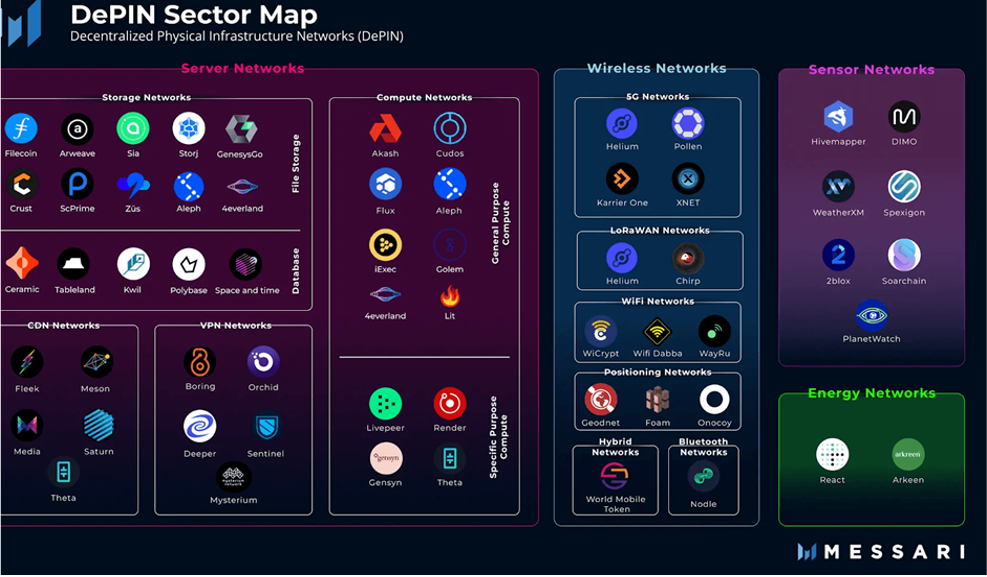
Clearly, the DePIN world contains many more projects. Among them, we haven't mentioned Storj, Sia, Pollen, React, or Arkreen, just to name a few examples. These projects vary primarily based on the field or type of network they aim to operate in. For example, while Storj and Sia belong to storage networks, Pollen falls under wireless networks, and React and Arkreen belong to energy networks.
The Long List of DePIN Benefits
The trend surrounding DePIN is becoming increasingly realistic each day. It seems that DePIN has the potential to become another acronym representing a phase of interest, where everything related to DePIN will experience significant value appreciation, similar to what we have seen with ICOs, DeFi, Metaverse, or NFTs.
However, that doesn't mean DePIN doesn't come with any benefits. On the contrary, here is a list of just the remarkable benefits that cannot be ignored in any conversation about DePIN:
Scalability: DePIN has the potential to scale much faster than its traditional counterparts. Some argue that their infrastructure can be built ten to a hundred times faster simply due to the decentralization among network participants. Furthermore, DePIN can scale globally in a permissionless manner, making it a more attractive solution with fewer barriers in the future. Cost Efficiency: The same principle of scalability also applies to cost-efficiency in production. The distribution among various market participants can ensure significantly cost-effective solutions compared to traditional alternatives. Uncensorability: If developed and deployed correctly, DePIN can be challenging to censor. With no single entity responsible for the project, it means regulatory bodies or governments cannot use this network for censorship. This is also due to the notion of collective ownership, a key assumption of DePIN. Collective Ownership: Speaking of collective ownership mentioned earlier, DePIN makes the interests of investors and stakeholders align harmoniously. This not only helps drive rapid adoption and development but also ensures that projects and solutions are better aligned with the needs of local markets. Integration with DeFi: Thanks to its decentralized and permissionless nature, DePIN can also foster innovation and improvements in the cryptocurrency world. It can support seamless micro-payments and integration with DeFi precisely because it's not limited like most traditional infrastructure solutions. Additionally, DePIN can offer more flexibility and versatility in the development and deployment stages. The barriers to entry for project participation are also expected to be lower compared to traditional solutions. The potential benefits list also includes self-reinforcing growth loops, community reinforcement, ownership, or custodial responses.
Limitations of DePIN
While the benefits of DePIN are evident, there are also challenges and limitations that need to be clearly defined. Some of these limitations are more theoretical, while others have been observed in the real world with certain projects. Some potential limitations of DePIN include:
Incentive Model: Many argue that the incentive model of DePIN has a high dilution, leading to false promises or enrichment for founders and members of the DePIN team. Intense Competition: Some may argue that the DePIN subsector is relatively small and has plenty of room to grow, thus lacking significant competition in the market. And while that may be true, the reality is that most new DePIN projects will compete against established giants like Amazon, Microsoft, or Google. It cannot be denied that it's a much more fierce competition. Failed Efforts: Helium and Filecoin, arguably the two most well-known cryptocurrencies in this space, experienced tremendous success in the bullish market of 2021. However, since then, both projects have faced difficulties, including opposition and accusations of market manipulations or blood-related relations. Like any cryptocurrency portfolio or subcategory, there are always drawbacks, not just benefits. The three limitations mentioned above are just some of them. However, over time, it will become evident that there will be many more limitations discovered as various projects attempt to dominate this emerging world of DePIN.
Conclusion
DePIN is becoming a new trend in the cryptocurrency world. Some have proposed that they have the potential to become a phenomenon similar to ICOs, DeFi, or NFTs. However, regardless of their tremendous potential and the incredible list of benefits they can bring to people, they will need to prove themselves. Most of these projects are either in their early stages or not significantly successful, meaning upcoming DePINs won't find success easily.

